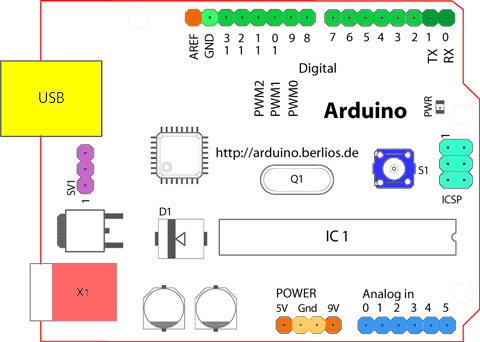
Looking at the board from the top down, this is an outline of what you will see (parts of the board you might interact with in the course of normal use are highlighted):

Starting clockwise from the top center:
|
ATmega168 (used on most Arduino boards)
|
ATmega8 (used on some older board)
|
In addition to the specific functions listed below, the digital pins on an Arduino board can be used for general purpose input and output via the pinMode(), digitalRead(), and digitalWrite() commands. Each pin has an internal pull-up resistor which can be turned on and off using digitalWrite() (w/ a value of HIGH or LOW, respectively) when the pin is configured as an input. The maximum current per pin is 40 mA.
In addition to the specific functions listed below, the Analog input pins support 10-bit Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) using the AnalogRead() function. Most of the Analog inputs can also be used as digital pins: Analog input 0 as digital pin 14 through Analog input 5 as digital pin 19. Analog inputs 6 and 7 (present on the Mini and BT) cannot be used as digital pins.
The text of the Arduino reference is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Code samples in the reference are released into the public domain.